"BALANCING THE SCALES"
GLOBAL MARKET SUMMARY
2024 | Q4
US
US equity markets ended 2024 with over 20% gains, driven by AI advancements and rate cuts. Consumer spending, which comprises two-thirds of GDP, helped sustain momentum while higher interest rates cooled the economy and brought inflation down from peak levels. President Trump’s re-election in Q4 boosted markets on pro-business policy expectations.
The ISM Non-Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) rose to 54.1 in December, signaling strong demand, while manufacturing activity showed stabilization. The Federal Reserve (Fed) cut rates by 100 basis points in 2024, ending the year at 4.25-4.50%, with fewer 2025 cuts projected due to persistent inflation risks and potential trade policy shifts.
Commercial real estate showed early signs of recovery, with property prices rising for six months but still down 7.4% year over year. Office prices dropped over 20% from 2022 peaks, while multifamily declined 12%. Tight financing conditions limited transaction activity, with lower-tier office properties underrepresented in commercial data due to limited financing and reduced transaction volume.
row-spacer
row-spacer
EUROPE
The Eurozone's GDP grew by 0.4% in Q3 2024, with annual growth at 0.9%, marking the strongest performance in five quarters. Spain and Ireland led growth, while Germany's GDP remained flat (0.1%) amid weak global demand and industrial challenges. Manufacturing continued to contract, with December’s PMI at 45.1, while the services sector stayed resilient, supported by strong tourism and hospitality demand.
The European Central Bank (ECB) cut rates by 25 bps at both October and December meetings, bringing the benchmark rate to 3%. President Christine Lagarde cited easing inflation (down to 2.4% in December) and slowing economic momentum as key factors. The ECB emphasized a cautious, data-driven approach, maintaining a restrictive policy to meet its 2% inflation target.
Political instability in Germany and France added uncertainty. Germany's coalition government collapsed in November, triggering new elections, while in France, a failed budget led to a no-confidence vote, unseating Prime Minister Michel Barnier. With no elections until mid-2025, President Macron faces gridlock in advancing reforms.
CHINA
China's economy grew 4.8% YoY in the first three quarters of 2024, with quarterly growth slowing from 5.3% in Q1 to 4.6% in Q3. This deceleration reflects weak domestic demand, reduced production, and low industrial capacity utilization.
The housing market showed mixed signals, with November home prices in 70 major cities down 5.7% YoY, a slight improvement from October’s 5.9% decline. However, home sales rose 4.6% YoY in November, marking the first growth since May 2023 and indicating early stabilization, especially in larger cities.
In late Q4, China rolled out major monetary and fiscal measures to boost growth. The People's Bank of China (PBOC) cut loan prime rates by 25 bps, reducing borrowing costs. Fiscal initiatives included increased spending, a large-scale debt swap for local governments, and a five-year, ¥10 trillion stimulus package (2.8% of GDP). These measures aim to ease financial pressures on local governments and fund critical infrastructure projects, addressing economic challenges to support recovery.
JAPAN
Japan's economy grew 1.2% (annualized) in Q3 2024, driven by strong domestic demand, tourism, and exports, despite weaker non-residential investment. Real wages fell 0.3% in November, but base salaries rose following the largest spring wage hike in decades, with further increases expected in 2025.
Business sentiment improved, with the Tankan manufacturing index rising to +14, supported by auto production and equipment demand. Exports grew 3.8% in November, aided by a weaker yen, though concerns remain over US trade policy.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) held its -0.1% short-term interest rate but signaled greater yield-curve flexibility, moving cautiously toward tightening. Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba pledged fiscal reforms and continued pro-growth policies.
COMMODITIES
The S&P GSCI rose 3.81% in Q4 2024, led by energy (+7.51%) and livestock (+5.82%), while industrial metals (-7.47%) weighed on performance. Within energy, all sub-sectors gained, while industrial metals saw declines, with copper and nickel dropping most. Precious metals also fell, with gold and silver prices declining.
Digital assets surged, driven by the launch of US spot Bitcoin ETFs and the Trump administration’s pro-cryptocurrency signaling. Bitcoin hit an all-time high of $108K in December before settling at $95K by quarter-end, reflecting renewed optimism for a favorable US regulatory framework.
US:
EUROPE:
According to data from Eurostat, economic growth across the Eurozone declined (-0.1% quarter over quarter) in the third quarter, as the region faced headwinds from inflation, rising interest rates, and tightened fiscal policies. Among the larger economies, France, Spain, and Belgium experienced growth while Germany contracted from persistent inflation, high energy prices, and weak foreign demand. Forward-looking economic indicators weakened for the region; the HCOB's final Composite PMI came in at 47.0. Manufacturing activity continued to contract and demand for services declined as consumers pulled back on spending. However, there was some signs of improvement in the manufacturing sub-indices tied to new orders and purchasing activity. Additionally, Eurozone unemployment remained at a record low of 6.4%; employment increased in both services and construction, offsetting weakness in the manufacturing sector. Overall, job vacancy rates have come down from their peaks but remain relatively high by historical standards.
After declining for much of the past year, the rate of inflation across the Eurozone rose to 2.9% in December. The uptick in inflation was primarily due to technical factors, as the impact of base effects and the timing of government subsidies overwhelmed slower price growth for other goods. (Note, core inflation, which doesn’t include energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco prices, ended the year at 3.4%, down from its 2022 peak.) In its last meeting of the year, the European Central Bank (ECB) reaffirmed its benchmark interest-rate policy and announced plans to phase out the last of its COVID-19 era bond-buying programs. The ECB also changed its language around inflation—from describing it as “expected to remain too high for too long,” to saying that it will “decline gradually over the course of next year.” In her statements following the meeting, ECB President Christine Lagarde assumed a more measured tone and argued against calls for imminent cuts to interest rates, stating that it’s too early to “lower our guard” and that the bank is “data dependent, not time dependent.”
CHINA:
China’s economic data in Q4 2023 presented a mixed picture. Industrial output experienced a significant rebound, growing by 4.6% (year on year) in October and an impressive 6.6% in November. This growth—the fastest pace since February 2022—underscored the sector’s recovery and contribution to the economy. On the other hand, already affected by a downturn in the property sector, reduced land sale revenue, and a slowdown in export manufacturing, consumer spending was further impacted by household deleveraging. Credit cards and mortgage loans saw a decline, indicating caution among consumers. Overall spending remained below pre-COVID levels, suggesting a slow and gradual path towards recovery.
In response to the property market's challenges, the Chinese government rolled out several initiatives, including reducing down-payment thresholds and mortgage interest rates, and easing restrictions on second-home purchases. Such measures were designed to ease financial pressure on homebuyers and stimulate market activity. Another notable development was the provision of low-cost financing, amounting to CN¥1 trillion, for urban village renovations and affordable housing projects. This significant investment is intended to support the real-estate sector, a critical component of China's economy. Early indications suggest a positive reception from homebuyers, particularly in major cities, signaling a potential upturn in the real-estate market.
The November 2023 meeting between Chinese President Xi Jinping and US President Joe Biden was a landmark event. Key topics included curbing illicit fentanyl production and military cooperation, alongside a dialogue on artificial intelligence emphasizing the importance of managing risks and safety issues. Described as ‘constructive and productive,’ the meeting underlined both leaders' desire for peaceful coexistence and the necessity of avoiding miscommunication. While it did not resolve all critical geopolitical issues, the meeting was viewed as a positive step towards stabilizing US-China relations. The meeting's conciliatory tone and focus on cooperation in specific areas signaled a potential easing of the strained relations between the two nations.
JAPAN:
Japan’s economy contracted at an annualized growth rate of 2.9% in the third quarter, as a decline in private consumption, which makes up more than half the economy, weighed on economic growth. Although nominal salaries rose year over year, higher prices and inflation wiped out the wage growth in real terms, negatively impacting consumers' purchasing power. In November, Prime Minister Fumio Kishida’s administration announced a new economic stimulus package (approximately $113 billion), aimed at helping households with rising costs. The packages included cuts to income and residential taxes, direct benefits to low earners, extended fuel and electricity subsidies, and funds to support the semiconductor sector.
Japanese business sentiment continued to improve during the quarter as measured by the Tankan survey. Results were especially strong among large manufactures; automakers' moods brightened as the industry benefited from a weak yen and an easing of supply constraints. Non-manufacturing sentiment was positive as well, improving for the seventh straight quarter; recovering inbound tourism gave a significant boost to non-manufacturers. Year to date through November, foreign visitors to Japan topped 20 million for the first time since 2019.
December data showed consumer core inflation trending downwards. Energy and fuel prices declined due to a combination of government subsidies and base effects. However, services inflation persists, driven primarily by demand for accommodations and food. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) ended the year with its low-interest polices in place. In his statement following the BOJ’s December meeting, Governor Kazuo Ueda cooled speculation about future rate hikes, stressing that more data is needed to confirm a positive wage-inflation cycle and the uncertainty surrounding inflation’s sustainability.
COMMODITIES:
The S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (SPGSCI) ended the quarter down with a total return of 10.73%, driven mainly by price gains for industrial metals and precious metals failing to offset weaker prices for energy, agriculture, and livestock. Contrary to Q3 2023, energy (16.74%; S&P GSCI Energy—SPGSEN) underperformed all other SPGSCI sub-index constituents, with sharply lower prices for crude oil, natural gas, and gas oil. These detractors to performance occurred despite output cuts from OPEC+. Agriculture (0.73%; S&P GSCI Agriculture—SPGSAG) ended the quarter with higher prices for soybeans, coffee, wheat, and cocoa failing to offset considerable price declines for sugar, corn, cotton, and Kansas wheat. The precious metals segment outperformed all other commodity constituents during the quarter (10.99%; S&P GSCI Precious Metals—SPGSPM), as both gold and silver achieved robust price gains during Q4 2023. The industrial metals segment realized a modest gain during the quarter (0.82%; S&P GSCI Industrial Metals—SPGSIM), as prices for aluminum, copper, and zinc offset weaker prices for nickel and lead.
Following a relatively quiet period in Q2/Q3 2023, the digital-assets market performed well during Q4. The premier digital token, Bitcoin, was up 57% in Q4 2023, while the second most-popular digital token, Ethereum (ETH), was up 37%, bringing the yearly returns to 155% and 91%, respectively. Speculation over the approval by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) of a US spot Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) was a significant driver of price movements during the period; this was subsequently approved in January 2024.
![UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113 [Converted]](https://www.crewcialpartners.com/hubfs/UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113%20%5BConverted%5D.png)
EUROPE
According to data from Eurostat, economic growth across the Eurozone declined (-0.1% quarter over quarter) in the third quarter, as the region faced headwinds from inflation, rising interest rates, and tightened fiscal policies. Among the larger economies, France, Spain, and Belgium experienced growth while Germany contracted from persistent inflation, high energy prices, and weak foreign demand. Forward-looking economic indicators weakened for the region; the HCOB's final Composite PMI came in at 47.0. Manufacturing activity continued to contract and demand for services declined as consumers pulled back on spending. However, there was some signs of improvement in the manufacturing sub-indices tied to new orders and purchasing activity. Additionally, Eurozone unemployment remained at a record low of 6.4%; employment increased in both services and construction, offsetting weakness in the manufacturing sector. Overall, job vacancy rates have come down from their peaks but remain relatively high by historical standards.
After declining for much of the past year, the rate of inflation across the Eurozone rose to 2.9% in December. The uptick in inflation was primarily due to technical factors, as the impact of base effects and the timing of government subsidies overwhelmed slower price growth for other goods. (Note, core inflation, which doesn’t include energy, food, alcohol, and tobacco prices, ended the year at 3.4%, down from its 2022 peak.) In its last meeting of the year, the European Central Bank (ECB) reaffirmed its benchmark interest-rate policy and announced plans to phase out the last of its COVID-19 era bond-buying programs. The ECB also changed its language around inflation—from describing it as “expected to remain too high for too long,” to saying that it will “decline gradually over the course of next year.” In her statements following the meeting, ECB President Christine Lagarde assumed a more measured tone and argued against calls for imminent cuts to interest rates, stating that it’s too early to “lower our guard” and that the bank is “data dependent, not time dependent.”
![UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113 [Converted]](https://www.crewcialpartners.com/hubfs/UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113%20%5BConverted%5D.png)
CHINA
China’s economic data in Q4 2023 presented a mixed picture. Industrial output experienced a significant rebound, growing by 4.6% (year on year) in October and an impressive 6.6% in November. This growth—the fastest pace since February 2022—underscored the sector’s recovery and contribution to the economy. On the other hand, already affected by a downturn in the property sector, reduced land sale revenue, and a slowdown in export manufacturing, consumer spending was further impacted by household deleveraging. Credit cards and mortgage loans saw a decline, indicating caution among consumers. Overall spending remained below pre-COVID levels, suggesting a slow and gradual path towards recovery.
In response to the property market's challenges, the Chinese government rolled out several initiatives, including reducing down-payment thresholds and mortgage interest rates, and easing restrictions on second-home purchases. Such measures were designed to ease financial pressure on homebuyers and stimulate market activity. Another notable development was the provision of low-cost financing, amounting to CN¥1 trillion, for urban village renovations and affordable housing projects. This significant investment is intended to support the real-estate sector, a critical component of China's economy. Early indications suggest a positive reception from homebuyers, particularly in major cities, signaling a potential upturn in the real-estate market.
The November 2023 meeting between Chinese President Xi Jinping and US President Joe Biden was a landmark event. Key topics included curbing illicit fentanyl production and military cooperation, alongside a dialogue on artificial intelligence emphasizing the importance of managing risks and safety issues. Described as ‘constructive and productive,’ the meeting underlined both leaders' desire for peaceful coexistence and the necessity of avoiding miscommunication. While it did not resolve all critical geopolitical issues, the meeting was viewed as a positive step towards stabilizing US-China relations. The meeting's conciliatory tone and focus on cooperation in specific areas signaled a potential easing of the strained relations between the two nations.
![UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113 [Converted]](https://www.crewcialpartners.com/hubfs/UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113%20%5BConverted%5D.png)
JAPAN
Japan’s economy contracted at an annualized growth rate of 2.9% in the third quarter, as a decline in private consumption, which makes up more than half the economy, weighed on economic growth. Although nominal salaries rose year over year, higher prices and inflation wiped out the wage growth in real terms, negatively impacting consumers' purchasing power. In November, Prime Minister Fumio Kishida’s administration announced a new economic stimulus package (approximately $113 billion), aimed at helping households with rising costs. The packages included cuts to income and residential taxes, direct benefits to low earners, extended fuel and electricity subsidies, and funds to support the semiconductor sector.
Japanese business sentiment continued to improve during the quarter as measured by the Tankan survey. Results were especially strong among large manufactures; automakers' moods brightened as the industry benefited from a weak yen and an easing of supply constraints. Non-manufacturing sentiment was positive as well, improving for the seventh straight quarter; recovering inbound tourism gave a significant boost to non-manufacturers. Year to date through November, foreign visitors to Japan topped 20 million for the first time since 2019.
December data showed consumer core inflation trending downwards. Energy and fuel prices declined due to a combination of government subsidies and base effects. However, services inflation persists, driven primarily by demand for accommodations and food. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) ended the year with its low-interest polices in place. In his statement following the BOJ’s December meeting, Governor Kazuo Ueda cooled speculation about future rate hikes, stressing that more data is needed to confirm a positive wage-inflation cycle and the uncertainty surrounding inflation’s sustainability.
![UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113 [Converted]](https://www.crewcialpartners.com/hubfs/UnderConstruction_shutterstock_415850113%20%5BConverted%5D.png)
COMMODITIES
The S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (SPGSCI) ended the quarter down with a total return of 10.73%, driven mainly by price gains for industrial metals and precious metals failing to offset weaker prices for energy, agriculture, and livestock. Contrary to Q3 2023, energy (16.74%; S&P GSCI Energy—SPGSEN) underperformed all other SPGSCI sub-index constituents, with sharply lower prices for crude oil, natural gas, and gas oil. These detractors to performance occurred despite output cuts from OPEC+. Agriculture (0.73%; S&P GSCI Agriculture—SPGSAG) ended the quarter with higher prices for soybeans, coffee, wheat, and cocoa failing to offset considerable price declines for sugar, corn, cotton, and Kansas wheat. The precious metals segment outperformed all other commodity constituents during the quarter (10.99%; S&P GSCI Precious Metals—SPGSPM), as both gold and silver achieved robust price gains during Q4 2023. The industrial metals segment realized a modest gain during the quarter (0.82%; S&P GSCI Industrial Metals—SPGSIM), as prices for aluminum, copper, and zinc offset weaker prices for nickel and lead.
Following a relatively quiet period in Q2/Q3 2023, the digital-assets market performed well during Q4. The premier digital token, Bitcoin, was up 57% in Q4 2023, while the second most-popular digital token, Ethereum (ETH), was up 37%, bringing the yearly returns to 155% and 91%, respectively. Speculation over the approval by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) of a US spot Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) was a significant driver of price movements during the period; this was subsequently approved in January 2024.
CPI
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) increased 0.3% in December, following a 0.1% increase in November. The all-items index rose 3.4% before seasonal adjustment over the previous twelve months. Over the past twelve months, the major contributors include transportation services, up 9.7% (driven by motor-vehicle insurance, up 20.3%), tobacco and smoking products, up 7.8%, and shelter, up 6.2%.

GDP
During Q3 2023, real GDP rose at an annual rate of 4.9% followed by a 2.1% increase in Q2 2023. The increase was driven by consumer spending and inventory investment; imports also increased. Overall, 14 of 22 industry groups contributed to real GDP growth in the third quarter; the value added from private goods-producing industries was particularly strong at 10.2%.

Retail Sales
Total retail and food sales increased 0.3% and 4.1% month-to-date and year-to-date ending November 2023, respectively. Total sales from September through November 2023 were up 3.4% compared to the same period one year ago; the percentage change over the same period was up 0.4%. Significant contributors include non-store retailers and food services and drinking places.

Unemployment

VIX
Market volatility, as measured by the VIX Index, had an average close in Q4 2023 at 15.29, trending up from Q3 (15.01) and down from Q2 (16.48). The index has dropped below its five-year average of 20.58, reflecting positive investor sentiment and a high level of comfort with the overall direction of the economy.
GMS Table Templates
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
||
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
||
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Large Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Mid Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Small Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
| U.S. Large Cap | U.S. Mid Cap | U.S. Small Cap | ||||
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Header | Header | |||
| Header | Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 | YTD |
|
Title1
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title2
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title3
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title4
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title5
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Header | Header | |
| Header | Q4 2023 | Q4 2023 |
|
Title1
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title2
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title3
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title4
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title5
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Country | Best Performing Style |
|
Title1
|
Value
|
|
Title2
|
Value
|
|
Title3
|
Value
|
|
Title4
|
Value
|
|
Title5
|
Value
|
|
Title6
|
Value
|
|
Title7
|
Value
|
|
Title8
|
Value
|
|
Title9
|
Value
|
|
Title10
|
Value
|
|
Title11
|
Value
|
|
Title12
|
Value
|
|
Title13
|
Value
|
Returns by style
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
||
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
||
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Large Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Mid Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Small Cap Growth
|
0%
|
0%
|
SECTOR Returns BY CAPITALIZATION
| U.S. Large Cap | U.S. Mid Cap | U.S. Small Cap | ||||
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
|
|
Basic Materials
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Consumer Goods
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Consumer Services
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Financials
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Health Care
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Industrials
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Oil & Gas
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Real Estate
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Technology
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Telecommunications
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Utilities
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Source: Russell Investments & Industry Classification Benchmark
|
||||||
|
Large Cap: Russell Top 200 Index | Mid Cap: Russell Mid Cap Index | Small Cap: Russell 2000 Index
|
||||||
us valuations
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2023 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2023 | |||
| US Large Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2023 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2023 | |||
| US Mid Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2023 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2023 | |||
| US Small Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
international valuations
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2023 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2023 | |||
| International Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2023 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2023 | |||
| Emerging Markets Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Source: Russell Investments Total Equity Profile
|
||||
non-us developed / emerging cap & style
| Q4 2023 | YTD | Q4 2023 |
YTD
|
||
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Large Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Mid Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
Small Cap Value
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Header | Header | |
| Header | Q4 2023 | Q4 2023 |
|
Title1
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title2
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title3
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title4
|
0%
|
0%
|
|
Title5
|
0%
|
0%
|
| Country | Best Performing Style |
|
Australia
|
Value
|
|
Brazil
|
Value
|
|
Canada
|
Value
|
|
China
|
Value
|
|
France
|
Value
|
|
Germany
|
Value
|
|
Hong Kong
|
Value
|
|
Indonesia
|
Value
|
|
Italy
|
Value
|
|
Japan
|
Value
|
|
Mexico
|
Value
|
|
Singapore
|
Value
|
|
Spain
|
Value
|
|
Thailand
|
Value
|
SECTOR Returns BY CAPITALIZATION:
| U.S. Large Cap | U.S. Mid Cap | U.S. Small Cap | ||||
| Q4 2024 | YTD | Q4 2024 | YTD | Q4 2024 |
YTD
|
|
|
Basic Materials
|
-14.2 | 2.1 | -12.4 | -11.0 | -5.7 | 3.6 |
|
Consumer Goods
|
-7.2 | 5.4 | -3.5 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 21.2 |
|
Consumer Services
|
14.8 | 35.3 | 2.9 | 14.7 | 0.3 | 8.1 |
|
Financials
|
7.1 | 32.3 | 6.3 | 30.9 | 3.8 | 16.6 |
|
Health Care
|
-10.5 | 5.4 | -7.5 | -5.2 | -7.4 | 3.0 |
|
Industrials
|
1.7 | 19.7 | -2.4 | 15.6 | 2.2 | 17.2 |
|
Oil & Gas
|
-5.9 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 18.1 | -1.6 | -6.1 |
|
Real Estate
|
-10.0 | -3.1 | -6.8 | 8.9 | -5.4 | 6.4 |
|
Technology
|
6.0 | 39.9 | 10.9 | 23.3 | 11.2 | 23.6 |
|
Telecommunications
|
2.5 | 22.8 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 1.6 | 24.0 |
|
Utilities
|
-7.8 | 18.6 | -2.0 | 29.2 | -4.7 | 7.3 |
|
Source: Russell Investments & Industry Classification Benchmark
|
||||||
|
Large Cap: Russell Top 200 Index | Mid Cap: Russell Mid Cap Index | Small Cap: Russell 2000 Index
|
||||||
GLOBAL EQUITY PERFORMANCE
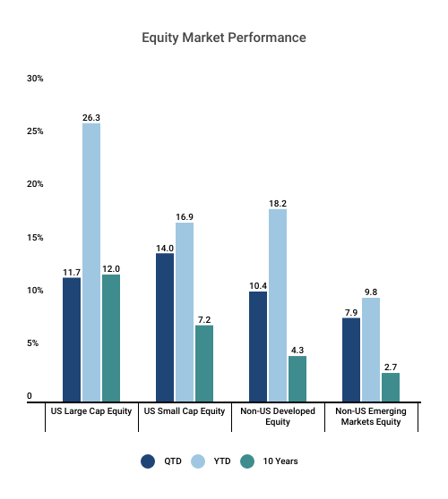
The MSCI EAFE and emerging-market indices fell 8.1% and 8.0%, respectively, while US large-cap equities gained 2.4%. International markets faced growth challenges amid European political uncertainty and US trade-policy concerns. Emerging markets declined on tariff fears, although China outperformed despite policy and trade uncertainties.
The MSCI ACWI fell 1.23%, with Israel (+13.38%) and the UAE (+13.08%) leading due to geopolitical developments. Austria (+1.07%) topped Europe, driven by banking sector strength, while Portugal lagged following its prime minister’s resignation amid a corruption scandal.
row-spacer
row-spacer
US VALUATIONS
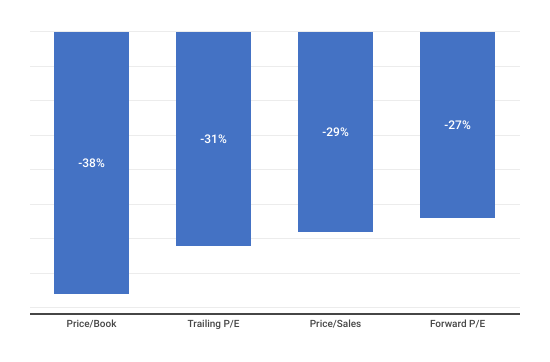
US equities are expected to grow Q4 2024 earnings by 11.9%, led by financials (+40%), communication services (+21%), IT (+14%), and consumer discretionary (+13%). Energy (-25%), industrials (-4%), materials (-2%), and consumer staples (-2%) are projected to decline. Analysts estimate 2024 earnings growth of 15%. Small-cap valuations expanded, while growth equities rose and value equities contracted. The S&P 500 remains overvalued, with a CAPE well above its historical average.
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2024 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2024 | |||
| US Large Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
23.4 | 40.3 | 23.8 | 40.0 |
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
9.0 | 16.4 | 9.2 | 19.9 |
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
16.9 | 31.3 | 17.2 | 30.3 |
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
5.1 | 1.9 | 5.7 | 1.8 |
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2024 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2024 | |||
| US Mid Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
22.1 | 43.7 | 23.3 | 41.9 |
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
8.9 | 14.7 | 8.7 | 15.9 |
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
16.3 | 28.5 | 16.6 | 26.5 |
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
7.8 | 11.4 | 8.2 | 10.8 |
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2024 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2024 | |||
| US Small Cap Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
29.3 | 16.1 | 28.1 | 163.1 |
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
8.1 | 14.2 | 8.4 | 14.4 |
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
13.3 | 19.9 | 12.7 | 19.5 |
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
24.3 | 33.9 | 25.4 | 33.0 |
INTERNATIONAL VALUATIONS
Non-US value equities saw slight compression, while growth equities stayed flat. International equities continue to trade at discounts to historical and US valuations. Emerging-market valuations declined further and remain cheap. Earnings growth is forecasted at 8% in Europe and Japan, and 14% for emerging markets in 2025.
| Quarter Ending 12/31/2024 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2024 | |||
| International Equity | Value | Growth | Value | Growth |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
13.3 | 26.8 | 13.3 | 24.7 |
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
6.4 | 12.9 | 7.1 | 13.4 |
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
10.5 | 21.8 | 10.9 | 21.8 |
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
5.7 | 3.2 | 7.0 | 4.3 |
| Emerging Markets Equity | Quarter Ending 12/31/2024 | Quarter Ending 9/30/2024 |
|
Price/Earnings Ratio
|
16.1 | 18.0 |
|
IBES LT Growth (%)
|
16.7 | 15.8 |
|
1 Year Forward P/E Ratio
|
13.1 | 13.9 |
|
Negative Earnings (%)
|
3.0 | 3.9 |
|
Source: Russell Investments Total Equity Profile
|
||
non-us developed / emerging cap & style: MSCI AC WORLD EX - US INDICES
(SOURCE: MSCI - DATA SOURCED 'AS IS')
| Q4 2024 | YTD | Q4 2024 |
YTD
|
||
|
Large Cap Value
|
-7.2% | 6.7% | Large Cap Growth | -8.0% | 5.4% |
|
Mid Cap Value
|
-7.5% | 3.7% | Mid Cap Growth | -7.3% | 3.4% |
|
Small Cap Value
|
-8.1% | 3.6% | Small Cap Growth | -7.2% | 3.1% |
| Country | Best Performing Style |
| Australia | Growth |
| Brazil | Value |
| Canada | Growth |
| China | Value |
| France | Growth |
| Germany | Growth |
| Hong Kong | Value |
| Indonesia | Growth |
| Italy | Value |
| Japan | Value |
| Mexico | Value |
| Singapore | Growth |
| Spain | Value |
| Thailand | Growth |
| United Kingdom | Value |
US SPREAD PRODUCTS
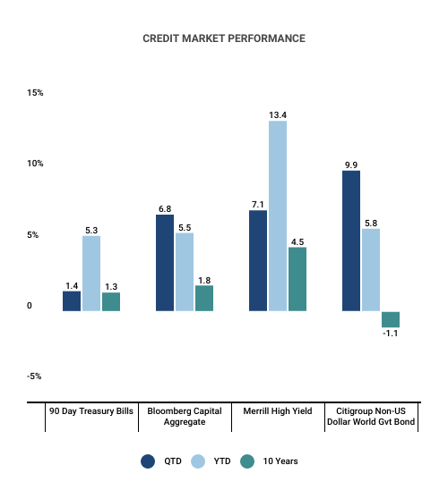
Investment-Grade Corporate Bonds: The market returned -3.0% for the quarter and 2.1% for the year, with quarterly losses driven by rising interest rates. Spreads tightened by 9 bps to 80 bps, near historic lows and 40 bps below the ten-year median. Lower-quality issues outperformed this quarter: Baa-rated corporates had the highest return at -2.8% (+2.7% annually) compared to A-rated (-3.3% quarterly, +1.7% annually) and Aa-rated (-3.0% quarterly, +0.9% annually). Quarterly issuance rose 10% YoY to $240 billion, totaling $1.6 trillion for the year (+25% YoY).
High-Yield Corporate Bonds: The market returned 0.2% for the quarter and 8.2% for the year, with quarterly gains from coupon interest and spread compression offset by rising rates. Spreads tightened by 8 bps (to 287 bps), near historic lows and 98 bps below the ten-year median. Lower-quality bonds led performance: Caa-rated corporates returned 2.3% for the quarter (15.1% annually), B-rated 0.3% (7.4% annually), and Ba-rated -0.5% (6.3% annually). Quarterly issuance rose 12% YoY to $50 billion, totaling $300 billion for the year (65% YoY).

hello world

GDP
During Q3 2023, real GDP rose at an annual rate of 4.9% followed by a 2.1% increase in Q2 2023. The increase was driven by consumer spending and inventory investment; imports also increased. Overall, 14 of 22 industry groups contributed to real GDP growth in the third quarter; the value added from private goods-producing industries was particularly strong at 10.2%.

Retail Sales
Total retail and food sales increased 0.3% and 4.1% month-to-date and year-to-date ending November 2023, respectively. Total sales from September through November 2023 were up 3.4% compared to the same period one year ago; the percentage change over the same period was up 0.4%. Significant contributors include non-store retailers and food services and drinking places.

Unemployment
A total of 494,000 jobs were created in the fourth quarter of 2023, which did not outpace the previous quarter’s gains of 710,000. The US economy added 216,000 jobs in November, which is below the twelve-month average monthly gain of 225,000. December’s notable job gains occurred within the following industries: government (+52,000), health care (+38,000), social assistance (+21,000), and construction (+17,000).
The unemployment rate remains unchanged from the previous quarter’s average at 3.7%. The number of unemployed persons (6.3 million) experienced minimal net movement as well. The labor force participation rate decreased by 0.3% in December (62.5%).

VIX
During Q2 2023, real GDP rose at an annual rate of 2.1%, following a 2.2% increase in Q1. The increase was driven by state and local government spending, non-residential fixed investment, and consumer spending, partially offset by a decrease in exports; imports also decreased. Relative to Q1, the second quarter experienced a slowdown in consumer and federal government spending alongside the decline in exports, which drove the Q2 deceleration of real GDP.
Charts
YIELD CURVE
US Treasury yields rose sharply during the quarter, with the curve steepening as yields increased 60-80 bps across maturities. The two-year note closed at 4.25%, the ten-year at 4.58%, and the 30-year at 4.78%; the ten-year note and 30-year bond ended the quarter near their respective year-to-date highs, having recently set year-to-date lows in mid-September. The two- to ten-year spread widened to +33 bps, the highest since mid-2022 but below the historical +85 bps average. Despite volatility, the yield curve has remained within a 3.5-5.0% range for over two years. Key drivers included solid economic growth, persistent core inflation, and expectations for a pro-growth policy agenda.


Love these and want more?
Enter your email address below and we will let you know when we add new resources.





